Kruskal’s algorithm finds a minimum spanning forest of an undirected edge-weighted graph. If the graph is connected, it finds a minimum spanning tree. It is a greedy algorithm that in each step adds to the forest to the lowest-weight edge that will not form a cycle.
This algorithm has a similar effect to Prim’s Algorithm, but it is different in the following ways:
Kruskal’s starts by the edges. It takes all edges, sorts them in increasing order, and then iterates over the edges, checking along the way to make sure they don’t form a cycle, until a spanning tree is made.
Explanation
Conceptually and visually, I’ve found Kruskal’s to be pretty easy to grasp. You get a set of nodes, you order the edges in increasing order, and then you iterate over them by checking if they form a cycle. If they don’t you add them to the minimum spanning tree and if they do you ignore them.
To do the above, you might already have a feeling for what other ADTs can be useful. To maintain a set of the lowest edge weight at all times, we would of course use a priority queue, specifically a min-heap. To check if a new edge would form a cycle, we would use a disjoint set.
Example
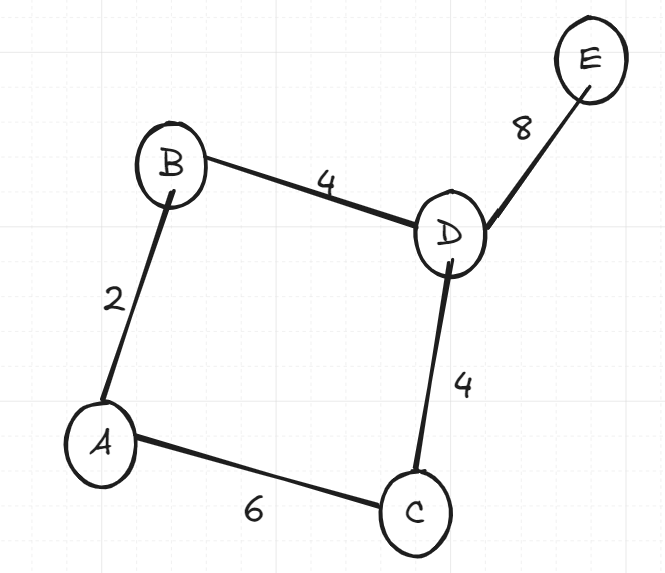
Try seeing if you can trace through what Kruskal’s would do on the above graph.
Answer
So first it would order edges by non-decreasing (increasing) order. So we have: AB, BD, CD, AC, DE. We then pop the AB edge off, since it’s the first in our priority queue. So, we add AB to our disjoint set and move on. Next, we have BD and CD. They both have the same value, however we will always have a way of differentiating in equal edge weight cases, and it’s usually alphabetical order, so BD comes first. We therefore add BD to our disjoint set and move to then add CD. We then have AC, but you will notice that adding AC would create a cycle, we therefore ignore it. We then add DE. Since we have a connected graph with edges, our algorithm is complete!
Time Complexity
Kruskal’s has a worst-case time complexity or , equivalently.